Organize Content Using Tags
Datasentinel uses InfluxDB, a time-series database, to store activity metrics collected from PostgreSQL instances.
InfluxDB supports Tags, which can be associated with measurements to index and filter metrics based on specific criteria. When used correctly, tags make it easier to organize data, improve query performance, and simplify analysis.
A tag is made up of a key and a value. (Ex application=crm)

Automatic tags
Datasentinel automatically creates a set of default tags for each monitored PostgreSQL instance
pg_instance
Concatenation of the server name and the instance name
pg_version
PostgreSQL version
server
Server name
database
Database name, if any
Defining custom tags
You can define custom tags to describe additional attributes of a monitored instance, such as the application it belongs to, the deployment environment, or the infrastructure provider.
Datasentinel does not impose restrictions on custom tags, allowing you to create and use tags that best fit your monitoring and organizational needs.
The following example shows JSON configuration file used to register an instance with a Datasentinel agent, including custom tag definitions.
Custom tags can also be defined when using the Agentless monitoring approach. In this case, tags are specified as part of the instance configuration, either through the UI or via the API.
To avoid issues, it is recommended to use only alphanumeric characters and underscores (_) in tag keys and values.
Session History and Tags
Datasentinel periodically samples active sessions.
During sampling, it automatically adds session-related tags based on data from pg_stat_activity.
application_name
Application name, if any
client_host_name
Server name or IP address
command_type
SQL command type
query_md5_id
MD5 identifier of the running SQL statement
user_name
User name
wait_event
Current wait event (I/O wait, lock, etc.) or CPU execution
wait_event_type
Event type (CPU, I/O, etc)

Why Use Tags?
Filtering
Tags allow you to filter based on specific criteria such as environment, application, or any other custom attribute.
This is especially useful when managing a large number of instances, as it helps you quickly narrow your focus to the systems relevant to your current task or analysis.
For example, if all production instances are tagged with environment=production, you can filter on that tag to view workloads for production systems only.

Data Analysis
The Data Analysis module provides tag-based statistics that offer a global view of activity.
For example, you can group top resource consumers by a tag such as the provider.
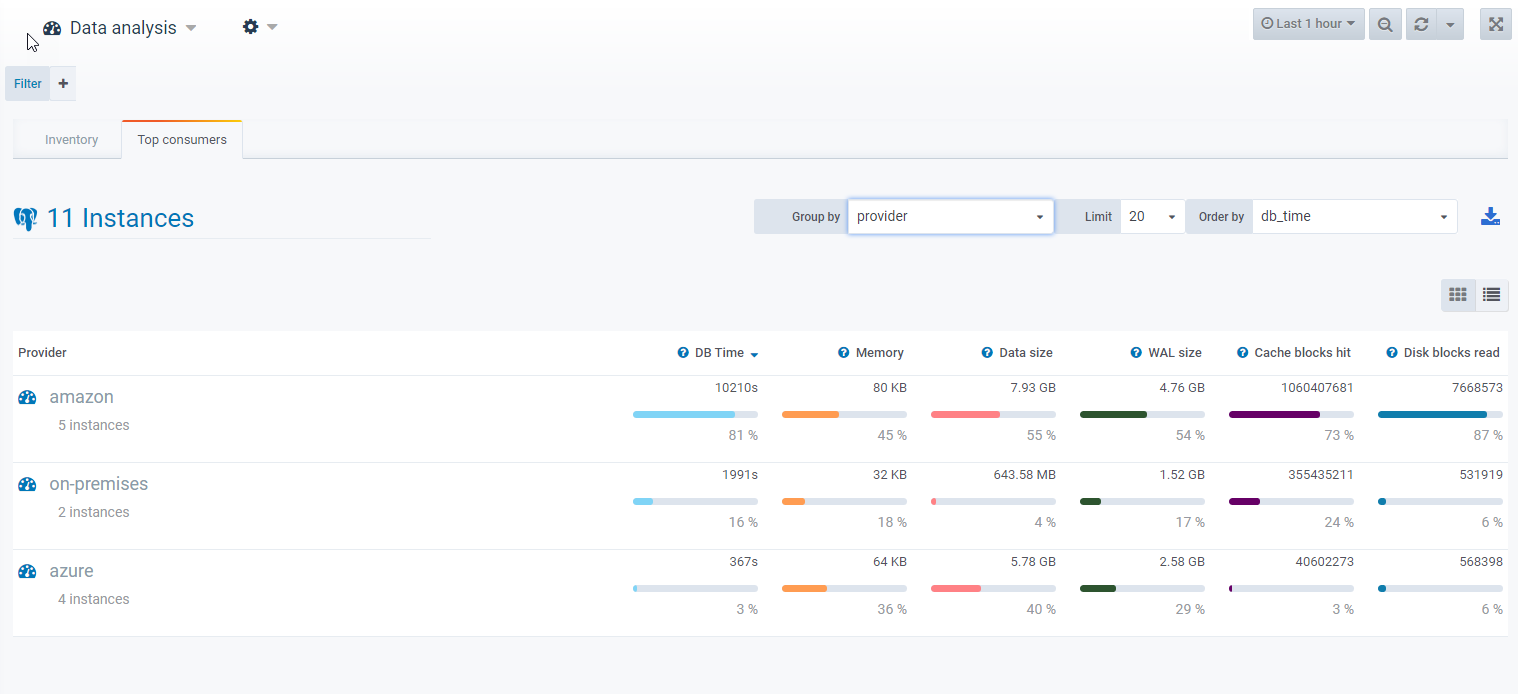
Consolidated Workload Analysis
Tags make it possible to extract aggregated statistics and obtain a global view of activity across multiple instances.
This is particularly useful when you want to analyze workloads at a higher level, rather than instance by instance. By grouping instances using a common tag, you can consolidate their workload and perform cross-instance analysis.
Common use cases include:
Listing the top SQL queries across multiple instances of the same application
Viewing overall activity for all instances running on a given server
Analyzing the consolidated workload of a primary instance and its read-only replicas
All of this can be done in just a few clicks, thanks to tags.

Role-Based Access Control
Datasentinel provides user management with support for role-based access control (RBAC).
Roles can be defined based on the value of one or more tags. When a role is associated with a user, access can be restricted to all or part of your PostgreSQL instance scope, depending on the tags assigned to those instances.
This makes it possible to enforce fine-grained access control aligned with your organization’s structure and environments.
Example:
You can create a user who has access only to instances tagged as environment=development.
Conclusion
Tags play a central role in Datasentinel, enabling efficient analysis, consolidated views, and tag-based access control.
A consistent tagging strategy is key to scaling monitoring across multiple PostgreSQL instances.
Last updated